Researchers develop novel vapor deposition technique based on continuous flash sublimation for rapid fabrication of all-inorganic perovskite solar cells
Researchers at NREL, BlueDot Photonics, University of Washington, Colorado School of Mines and Rochester Institute of Technology have developed a vapor deposition technique based on continuous flash sublimation (CFS) to fabricate all-inorganic perovskite thin films in under 5 minutes in a continuous process. The adoption of the proposed approach may also result in higher power conversion efficiencies of perovskite solar cell.
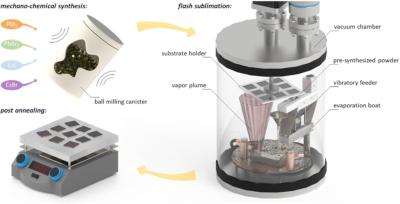
Schematic illustration of the continuous flash sublimation (CFS) approach consisting of a mechano-chemical synthesis of the source powder (here CsPb(IxBr1−x)3), the high-throughput deposition process in a home-made evaporation system, and a short post-annealing treatment to improve thin-film quality. Image from Journal of Materials Chemistry A
The team described the new technique as a non-batch process that solves two problems associated with the use of established vapor processing in perovskite material manufacturing – the slow speed of deposition and the non-continuous nature of batch processing.